

This article has been edited by Mansi Bathija and written by Ayushi Yadav , a fourth-year law student from Banasthali Vidhyapith, Rajasthan. In this article, she has discussed the basics of the Indian income tax act of 1961.
Tax is the mandatory financial charge demand by the government on pay, product, administrations, exercises or exchange. Taxes are the fundamental modes of income for the government, which are used for the welfare of the general population of the nation through government strategies, arrangements, and practices.
There are references for taxes in ancient writings like Manusmurti and Kautilya Arthashastra. It was initiated in India in 1860 for the first time to defeat the financial crisis of 1857. Accordingly, it is the income tax Act 1961 which is at present operative in India
The basis of every legislation in India is rooted in the constitution. As per article 265 of the constitution, no tax must be levied or collected except by the authority of law. There are various other provisions under the constitution that distribute the power.

Entry 82 of List I of Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India grant power on Parliament to impose taxes on income other than agricultural income. In this way, Income Tax is under the Union list and therefore Central Government is in charge of the collection of income tax.
The Central Government has the authority to collect taxes on income aside from the tax on agricultural income, which is being collected by the State Government. Entry 46 of List II of the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India lays down that the State Government has the authority to collect taxes on agricultural income.
Income tax is a tax on the income of an individual or an entity. Income tax is the main source of income for the government to carry out its functions. The jobs of government are not just restricted to defense, law, and order, etc., but it also has to undertake activities like welfare and development under sectors of health, education, rural development, etc. the government also has to pay for its own administration. All of these activities need huge public finance which is raised by the collection of taxes.
Taxes are broadly divided into two categories- Direct and Indirect taxes.
Income tax is a direct tax imposed on an individual. Estate and wealth tax were also direct taxes, however, these are abolished now
Indirect taxes that were imposed in India are customs duty, central excise duty, service tax, sales tax, and value-added tax.
As of now GST has been implemented and has made all the other indirect taxes obsolete.
As per Section 2(9) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, states that assessment year means the 12 month period beginning on the 1st day of April every year. The assessee is required to file the income tax return of the previous year in the assessment year. As per S.2(34) of Income Tax Act, 1961, unless the context otherwise requires, the term “previous year” means the previous year as defined in section 3.
As per Section.3 of Income Tax Act, 1961, the term “previous year” means the financial year immediately preceding the assessment year

Say, for example, the year starting from 1st April 2018 and ending on 31st March 2019 is the assessment year 2018-19, the previous year would be 2017-18. The rates of assessment year are taken into consideration.
A person is defined under section 2(31) of the act. The term ‘person’ includes –
Any individual who has income earned or losses incurred, and is liable to pay taxes on these to the government in a particular assessment year, is an assessee.
Categories of the assessee –
The Income Tax Act does not define the term Income but section 2 (24) of the Act describes the various receipts which are included under the ambit of income.
Accordingly, the section provides that :
Income is classified under 5 main heads under section 14 of the act
Agricultural income is any rent or revenue by means of cash or in-kind, derived from a land, which is used for an agricultural purpose and land should be situated in India.
Income from agricultural should be produced by a cultivator or a rent receiver of that produce in-kind, which can be fit to take that into the market.
The income should be derived from the sale by a cultivator or a rent receiver of that product which is produced or received by him, no process can be performed other than the process to render it fit for the market. You can read more about agricultural income here.
The income of a non-resident person or a foreign company is only taxable to the extent it arose in India. However, under section 9 of the income tax act, other provisions lay down the criteria as to why certain incomes are deemed to accrue in India even though they might actually arise out of India.
Business connections – the term business connections has not been defined in the act but various judgments and circulars have emphasized on the meaning of it.
As per the circular no. 23 of the income tax. Examples of non-resident having business connections in India have been given-
The taxation laws classify taxable persons under three categories
There are various tests to determine the residential status of a person
Test 1 – If the person is residing in India for 182 days, not necessarily at a stretch, in the preceding previous year, he is said to be a resident of India.
Test 2 – If the person is residing in India for 365 days or more in the previous 4 years and 60 days in the immediately previous year, he is said to be a resident.
An individual is not an ordinary resident if
Test 1 – he has not resided in India for 9 out of the 10 previous years preceding that year
Test 2 – if the individual has not resided for 729 days or more in India in the 7 previous years
Test 3 – a Hindu undivided family whose manager has fulfilled above conditions
Let’s understand this with an example
Question . Mr. John, a foreigner came to India for the first time in 2014 and settled here. He wants to file his income tax return for the assessment year 2015-16 and 2016-17. Determine his residential status for the said two years.
Answer . For the assessment year 2015-16, the previous year is 2014-15
For the previous year 2014-15, he is a resident, because, in the year ending 31st March 2014, he has stayed in India for more than 182 days.
For the previous year 2015-16, he is a resident for he has stayed in India for more than 182 days in the year ending 31st March 2016
For the previous years 2014-15 and 2015-16, he is not an ordinary resident because he is non-resident India for 9 out of 10 previous years preceding previous years and he has not resided in India for 730 or more days during 7 preceding previous years.
As per section 6(3) of the income tax act, a company is said to be a resident of India if either of the following conditions is fulfilled-
Place of effective meaning is the place where all the important key managerial and commercial decisions for the conduct of business are made.
Payroll taxes are Medicare and social security taxes, employers withhold half of these taxes from employee’s wages. Medicare taxes are a contribution to medical benefits for the person above the age of 65. Social security taxes are for the benefits of the retired person or disabled person or for their dependents. These two taxes are called as FICA tax, i.e., Federal Insurance Contribution Act Tax, which is defined by Internal Revenue Service. These taxes are paid to the Federal or State authority.
If a person is self-employed then he doesn’t need to pay FICA tax, but a Self-employed Tax needs to be pay by him.
FICA Tax rate is equal for employers and employees. Self-employed tax rates are different from FICA tax rates.
The income tax calculator is available for quick and easy access to basic tax calculation for the public. It does not assure the taxpayer for an exact payable tax. Some basic details have been provided to the calculator.
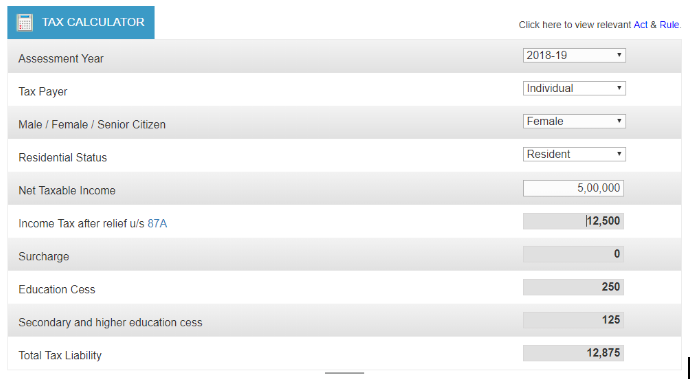
In the above image, as per details are given to the calculator total tax liability of a female individual is Rs. 12,875.
Form 16 is a Tax Deduction at Source Certificate issued by the Income Tax Department for the tax deduction of an employee by the employer on their behalf. It is a mandatory certificate for the taxpayers. This deduction can be reimbursed by the employee later. This form contains details of the transaction between the deductor and the deductee. The certificate must be issued immediately after the Financial Year or before the 15 June of the next year. TDS certificate should be issued every year.
Form 16 contains two parts – Part A and part B.
Part A – Part A of Form 16 contains :
If an employee changes his employment during one financial year, then the employer will issue different Part A of Form 16.
Part B – Part B is the annexure of Part A which contains details in regards to the computation of taxable income, this Form will attach along with Part A of Form 16 and if the employer has more than one job in any Financial Year than he has to attach more than one Form. Part B has components:
As per the Black Law Dictionary (9th Edition) An Income Tax form on which a person or entity reports income, deductions, and exemptions and on which tax liability is calculated.
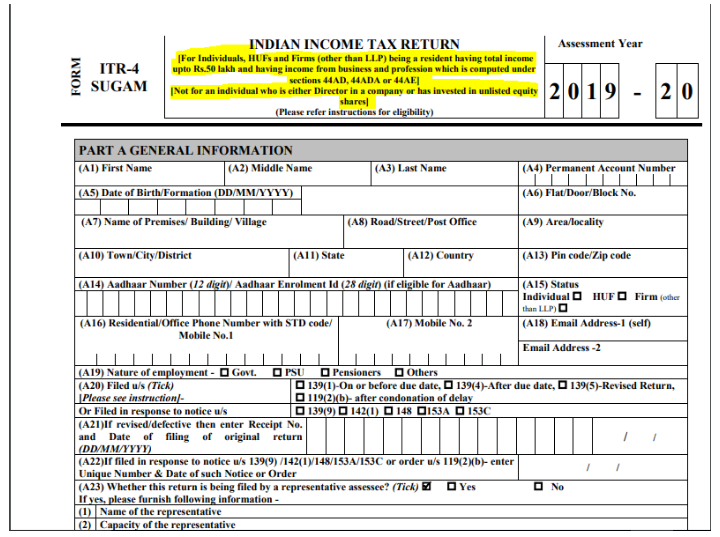
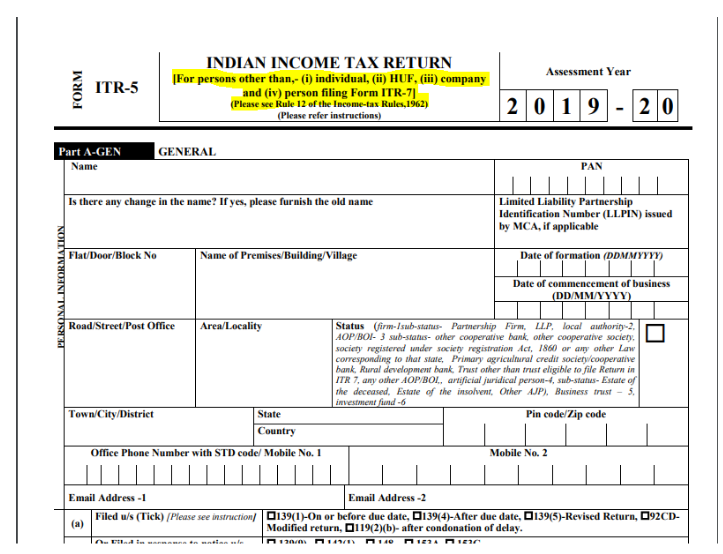
Income Tax Return (ITR) is a statement of tax and income, which an individual files to inform the government that how much income he has earned in a financial year. ITR should be filed before the last date, i.e., 31st July. There are different ITR form filed by an individual as per their applicability, and the eligibility of a person is mentioned in the form. There is a total of seven ITR forms which we will discuss one by one.
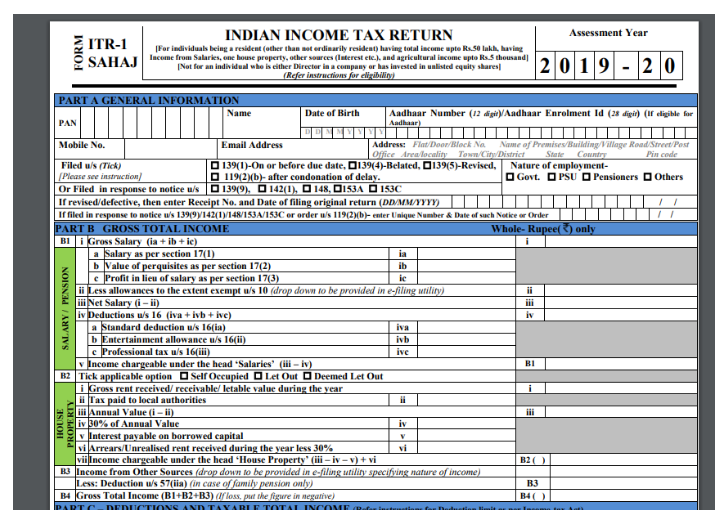
This form is divided into five parts, i.e., Part -A, Part-B, Part-C, Part-D, and Part-E, which requires some details in terms of income.
Income Tax rates divide into four slabs, i.e., 0%, 5%, 20% and 30%.
Age of the individual
Tax rate Slab applicable
Limit on Income
12,500 + 20% of total income
1,12,500 +30% of total income
2,50,001 to 5,00,000
5,00,001 to 10,00,000
10,000 + 20% of total income
1,10,000 + 30% of total income
3,00,001 to 5,00,000
5,00,001 to 10,00,000
1,00,000 + 30% of total income
5,00,001 to 10,00,000
As per this slab, an individual is liable to pay taxes or tax deducted from their salary.

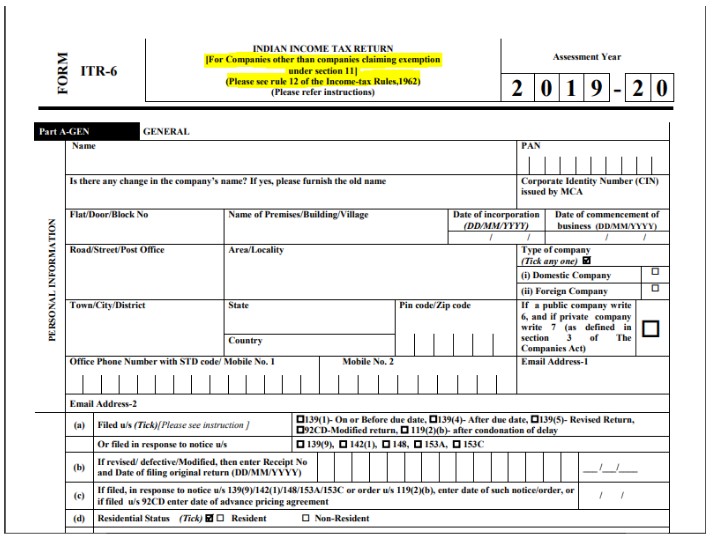
Corporate income tax is levied by the government on the profits of the companies. The tax rate paid by companies varies every year by the Income Tax Department. There are two types of Company explained under the Income Tax, i.e., Domestic Company and Foreign Company.
Domestic Company.- Domestic Companies are those which are registered under the Companies Act of India. A company can be a Public Company or a Private Company. I also include those companies which are situated or registered outside India but having control and management completely in India.
Foreign Company.- Foreign Companies are those which are not registered under the Companies Act of India and having control and management completely outside India.
Now, under Corporate Income Tax these both companies are liable to pay taxes. In the case of Domestic Company, tax is levied on universal income but for Foreign companies, only that income is taxable which is earned within India.
Income earned from the Company included-
Income Tax Rate of the company depends on the turnover of the company during the Financial Year.
Income Tax Return form file by a company is ITR-6 and ITR-7. As per Income Tax, requirement companies have to audit their accounts and submit it along with ITR form. This audit is known as Tax Audit .
Tax is a mandatory charge levied on a person by the government, as we have discussed what taxes are paid by a person and how he can calculate his payable tax. There are a number of Provisions provided under law for taxpayers as per their requirements. The government has provided various forms to pay income tax whether a person is an individual or HUF or a company or he is an ordinary resident or non-ordinary or non-resident person, as per their applicability they can file income tax.